Ubuntu versions, and official flavors, have different lengths of time that they’re supported. Today, we’ll learn how to tell how much longer you have Ubuntu support and what you can do about it.
Every two years, Ubuntu releases a LTS version. That means “Long Term Support” and the support length for that is usually 3 years, and then it enters ESM, which means Extended Security Maintenance. Except when they don’t, and you get 5 years of support and 10 years of ESM.
Ubuntu’s official flavors have LTS versions that also come out every two years. Those are supported for three years and then you have no access to the flavor-specific updates unless you update to the newest LTS version of said official flavor.
Every six months, Ubuntu releases an ‘interim’ release. These releases are supported for nine months, which means you have a three month window to upgrade to the next version before the upgrade window closes. These releases also explore new versions of software that will make it into the LTS releases.
LTS releases are always YY.04 releases, but not all YY.04 releases are in fact LTS releases. They’re only LTS releases if the year of release was an even year. So, 18.04 and 20.04 are all LTS releases and there won’t be another LTS release until 22.04 – which, according to Ubuntu’s versioning format will be in April of 2022.
Confused yet?
I can’t blame you if you are! After all, unless you spend all your time learning about this sort of stuff then you’re not going to remember that. At best, you have the “proper” configuration and you upgrade when your OS tells you to upgrade. If you’re using an interim release and miss that upgrade notice then it can be quite an ordeal to upgrade to a new version.
Let’s figure this out.
How To: Check Ubuntu Support Status
Fortunately, you can check your support status pretty easily. The results may be confusing, but you’ll figure it out.
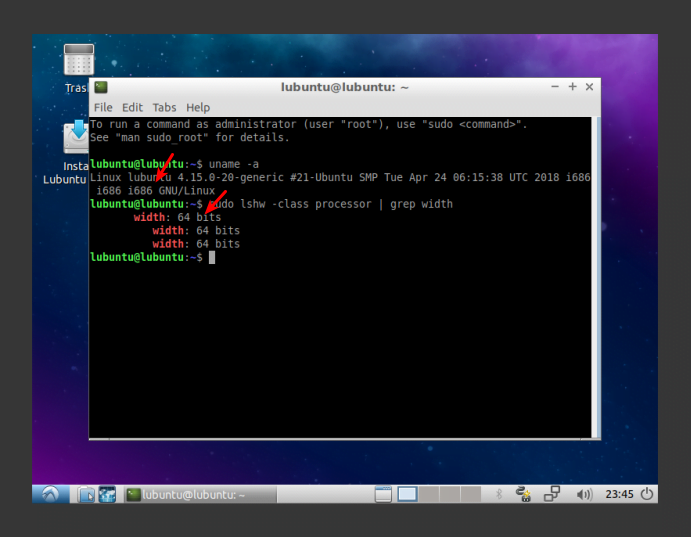
Like so many articles, let’s crack open the terminal. Just use your keyboard and press
If you’re using 18.04 or older, then you use the following command:
1 | ubuntu-support-status |
If you’re using 18.10 or newer, then you’d use this:
1 | ubuntu-security-status |
Your output will look something like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | kgiii@kgiii-msi:~$ ubuntu-security-status 2030 packages installed, of which: 1449 receive package updates with LTS until 4/2025 571 could receive security updates with ESM Apps until 4/2030 2 packages are from third parties 8 packages are no longer available for download |
Which, as you can see, says I have support until 2025. If I had ESM enabled, that’s software from the Ubuntu Advantage program, then I’d have security updates even longer. As you may recall, that requires Snap apps, and I’ve chosen to disable Snap Applications. So, obviously I won’t be doing that whole ESM thing.
Not that it matters with the ESM, because I’m using Lubuntu. Where it says 2025, I have to assume “official support” to only last until 2023 – three years of support. Now, you can keep using an official flavor beyond those three years, it’s just that the official flavor parts won’t be getting any additional updates. That’s generally considered a Bad Idea®. But, you can do so, and that’s why the date for ending Ubuntu support is later than it really is.
Anyhow, that should make it more clear. You should find the end date of your OS’s support and keep that in mind. You should make plans to upgrade in a timely manner, because security updates are important to you and the rest of the ‘net.
NOTE: When your computer isn’t upgraded you’re a threat not just to yourself. You risk becoming compromised and becoming part of a botnet, spamming relay node, or worse. So, keep things upgraded. Thanks!
Like always, thanks for reading. You can participate by contributing articles, donating, or sharing the links with others. You can also sign up for the newsletter. I promise, I won’t send you any spam!